ACE Inhibitors or ARBs: Which to Prescribe?
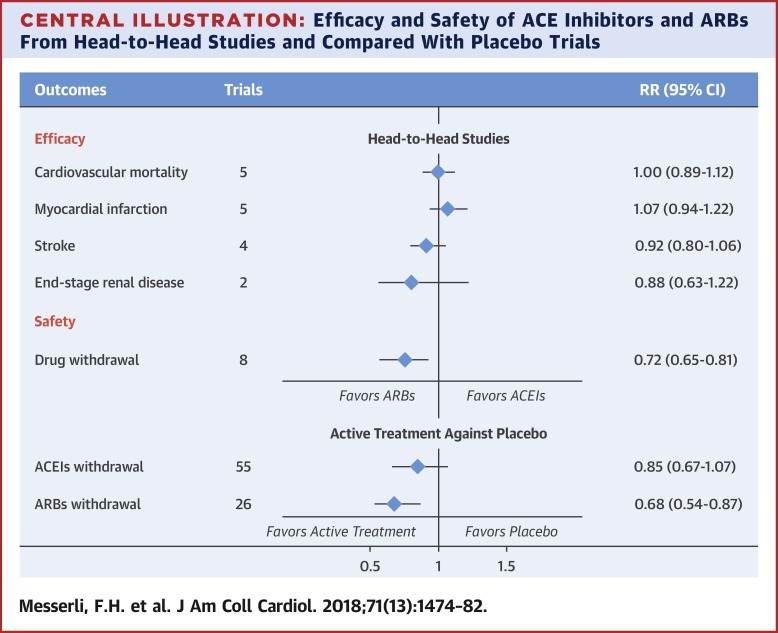
Many dialysis patients, including patients on frequent home hemodialysis, have been diagnosed with heart failure. In one large study, 31% of patients who initiated home hemodialysis already had heart failure.1 One of the cornerstones of pharmacologic therapy for heart failure is renin-angiotensin system blockade, which may be achieved with either angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs). In most clinical practice guidelines, ACE inhibitors are recommended as first-line therapy, while ARBs are recommended as a second option for patients who cannot tolerate an ACE inhibitor, typically because of a dry, persistent cough and atypically because of angioedema.
Learn More